Are you curious about the Korean language? Or maybe you want to know the difference between how people speak in South Korea and North Korea? You’ve come to the right place!
Apart from learning facts about Korea and Korean culture, it’s also good to know some important information about Korea’s language.
We’re going to cover everything you need to know about Korean. We’ll also include some resources you can put into practice if you decide you want to learn the language, or just know how to speak Korean for a trip out to the Korean Peninsula.
Here we go!
Contents
- 1 Korean
- 2 Koreans
- 3 The Korean language
- 3.1 Is Korean a language?
- 3.2 The Korean Language Family
- 3.3 Countries that speak Korean
- 3.4 How many people speak Korean?
- 3.5 Korean language dialects
- 3.6 Korean Accent
- 3.7 Dialect Influences
- 3.8 How many languages are spoken in South Korea?
- 3.9 What language is Korean most similar to?
- 3.10 What type of language is Korean?
- 4 Korean Languages
- 5 Official Language of Korea
- 6 History of the Korean language
- 7 Hangeul Alphabet and Writing System
- 8 History of Korean Language and Literature
- 9 How to Speak Korean
- 10 How to Learn Korean
- 11 What is Korean vocabulary like?
- 12 Conclusion
Korean
The word “Korean” can refer to the Korean language or a Korean person.
Koreans
The word “Koreans” means “Korean people.” However, it can have a slightly different meaning depending on where the person was born.
Koreans born in Korea
A Korean is someone who was born in North Korea or South Korea. Both 한국인 (hangugin) or 한국 사람 (hanguk saram) mean “Korean person”.
The word for a South Korean person is 남한 사람 (namhan saram). The word for North Korean person is 북한 사람 (bukhan saram).
Koreans born outside of Korea
Overseas Koreans are called 교포 (gyopo). If you want to specifically refer to a country that an overseas Korean is born in, you will use the Korean + country.
For example, a Korean American would be 한국계 미국인 (hangukgye migugin). That translates to “Korean American.” The 계 (gye) added to the end of 한국 (hanguk) means “of that country’s decent.”
The Korean language
So, what language do Koreans speak? They speak the Korean language which is made up of its own alphabet and writing system. It is spoken by almost 80 million people and is the official language of South and North Korea. It’s also an official language in the Yanbian region in China.
The word “Korean” can refer to the language, people, or an aspect of the culture. Typically when people say Korean, they are referring to South Koreans. However, Korean can also refer to anything in the Korean peninsula and its history.
Is Korean a language?
Yes, Korean is the language spoken by both North Koreans and South Koreans. They have different dialects (South Korean dialect and North Korean dialect), but the fundamental parts of the language are the same. A North Korean and South Korean would be able to communicate with each other fairly easily.
The Korean Language Family
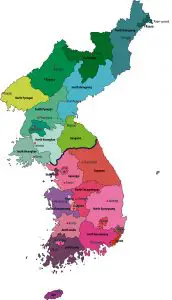
Korean has its own language family called Koreanic. The Korean language consists of mainland Korean plus the dialect of Jeju Island. There are many dialects in Korean, such as the Seoul dialect, and Jeju is the most significantly different.
The Korean taught in classrooms and used by Koreans today was formed a few hundred years ago. Before that, older versions of the language were used.
Countries that speak Korean
Korean is the official language in both North Korea and South Korea. North Korea is known as DPKR (Democratic People’s Republic of Korea). South Korea is known as ROK (Republic of Korea).
It is also the official language in the Yanbian region of China. It’s spoken in many other regions in the world, but not as the official language.
How many people speak Korean?
Korean is spoken by more than 75 million people worldwide. The majority of the speakers live in South and North Korea, where it is the official language.
Outside of the Korean peninsula, the cities with the most Koreans in them are Beijing, Los Angeles, New York, Tokyo, Osaka, Atlanta, and Sydney. The United States, China, and Japan have the largest total number of Korean speakers.
Korean language dialects
The Korean language has nine different dialects. Both South and North Korea have their own standard Korean dialects, which are used in an official setting. In the South, it is Seoul’s dialect. In the North, it is Seoul’s dialect mixed with Pyeongyang’s region’s dialect.
Additionally, there are two more dialects in use in North Korea and five more dialects in use in South Korea. Of these regional dialects, the most different from standard Korean is the dialect used on Jeju Island.
Because of all of the time apart after the Korean War, the dialect used in North Korea has become quite different from the dialect used in South Korea. This is because both regional dialects were influenced by the other countries involved in the Korean War.
Korean Accent
Both North and South Korea use the same language, so they don’t have difficulty understanding one another. However, both countries have distinct accents. North Korea’s accent is stronger than the South’s.
Though the two countries can understand each other’s languages, it’s easy for them to identify with each other. Someone may be identified as North Korean just by their accent.
Dialect Influences
South Korea’s version of the language was influenced by English, and North Korea’s version of the language was influenced by Russian. Not only have their vocabularies changed, but their pronunciation has as well.
Besides the Korean peninsula, there are many native Korean speakers living abroad. The regions with the biggest Korean populations are the United States, China, Japan, Canada, Uzbekistan, Vietnam, Russia, Australia, and Kazakhstan.
How many languages are spoken in South Korea?
There is one official language spoken in South Korea, with five different dialects. Seoul dialect is the standard version that is used in speeches and used on news reports.
Some other commonly spoken languages in South Korea are English, Japanese, Chinese, and Russian.
What language is Korean most similar to?
Korean shares some similarities with both the Japanese and Chinese languages. Korean is similar to Japanese in terms of grammar and sentence structure. They both also have their own unique writing systems that are fairly easy to learn. However, the Japanese writing system also uses adopted Chinese characters called Kanji. Most Japanese words are written with Chinese characters.
The Korean writing system also uses something similar called Hanja, but they’re not used as often as in Japanese.
Many words in Korean have Chinese origin, so in that way, Korean and Chinese languages are similar. However, there are no tones in Korean like there are in Chinese.
Some modern-day newer Korean words, sometimes called Konglish, are adapted from languages such as English and German.
What type of language is Korean?
Korean is a phonetic language, meaning that you can sound out individual letters to make words. It has an alphabet with individual sounds for each letter, and the letters are read from left to right and top to bottom. There are individual syllables. Many native English speakers can learn the alphabet (Hangul) in about 1-2 hours.
Korean Languages
Today, there are 2 Korean languages used in the Korean peninsula. This is because, as we all know, the Korean peninsula is occupied by two countries, namely South Korea and North Korea.
South Korean Language
The South Korean language is called and widely known as 한국어 (hangugeo). This is the language most Korean learners are learning.
North Korean Language
The other language used in the Korean peninsula is the North Korean language. This is called 문화어 (munhwaeo).
Official Language of Korea
Korean is the official language of South Korea, and has a few organizations that support it.
National Institue of Korean Language
The National Institute of Korean Language helps to improve the Korean language. It does this by doing research and creating Korean language policies for the correct usage. They provide a useful dictionary that also has audio.
Test of Proficiency in Korean (TOPIK)
The official test of the Korean language is the TOPIK. This test is often required to work at Korean companies or to obtain a visa in Korea.
History of the Korean language
The earliest forms of the language have likely existed since the Stone Age. However, the specific history of the language remains a mystery.
Some claim that the various groups of people occupying the Korean peninsula eventually became one, forming a single language. This likely happened during the unification period in the 6th to the 14th century. And in the 15th century, the modern Korean language we all know was formed.
The language used to be written with Chinese characters, which was one of the many writing systems used for representing Korean sounds. However, the Chinese characters couldn’t precisely represent the sounds of the Korean language. During the reign of King Sejong, the Korean writing system called Hangul, which was originally called 훈민정음 (hunminjeongeum) was completed. Hangul is the writing system that best encapsulates the sound of the Korean language.
What is Hanja?
Chinese characters were introduced to the region in the first century BC. They were adapted to the language and became known as Hanja (한자). It was used as a means of writing Korean.
Hanja Usage
These Chinese characters were officially used in Korea until just 100 years ago, when Hangul, the Korean alphabet, finally became popular as the writing system. Even today, you can still see some Hanja used by South Koreans, especially in official documents.
In North Korea, however, Hanja has officially not been used since 1949. Many words borrowed from the Chinese have been replaced with native Korean words by North Koreans. The Chinese loan words are still used and are written in Hangul now. You can find Hanja in special situations, such as dictionaries.
Hangeul Alphabet and Writing System
The Hangul system was created by King Sejong in 1443. In North Korea, it’s called Joseongul. It became the most important writing system in both North and South Korea after World War 2 and the Korean War.
There are 14 consonants and 10 vowels in the Hangul (also spelled “Hangeul”) writing system. These are then combined into blocks to form words. Writing basic Korean letters is fairly simple. Many of the letters in the alphabet are only a single line or two.
One convenient aspect of the writing system is that many of the letters in the alphabet have similar equivalent sounds in English. That makes it to learn the letters and sounds fairly easily. Many people can learn basic Hangul in about 1 hour.
History of Korean Language and Literature
One of the parts of Korean culture that has been the most impacted by the evolution of Korean is literature. While some form of literature, such as oral literature, has existed since the discovery of the earliest form of Korean, its current form of literature is newer.
Initially, when Chinese characters were introduced to Koreans, all of the literature, poetry, and so on were written in Chinese characters. So technically, most of the Korean literature before the 20th century was written in the Chinese language, even after Hangul was created.
First written poetry
The first form of poetry was discovered during Silla Dynasty (57 BC – 935 AD). However, the form of poetry that best lasted until nearly the modern days, called sijo, was created during Joseon Dynasty (1392–1897). The first written historical records, and thus the birth of prose in Korea, date back to Goryo Dynasty (918–1392). All in all, Korean literature’s origins can be traced all the way back to Old Stone Age.
First Korean novel
The first modern Korean novel was published in 1917. A lot of the early period of modern Korean literature was influenced by Western poetry, which was translated into Korean. By the 1930s, modern Korean literature reached maturity and has continued evolving ever since to what literature in the two Koreas looks like today.
How to Speak Korean
You can learn to speak Korean without learning Hangeul (the Korean Alphabet). However, it will be much easier and faster if you first learn the alphabet. You will be able to pronounce words more accurately and understand what you hear more easily.
Does the Korean language have tones?
No, Korean doesn’t have tones like Chinese. If you can read Hangul, it’s easy to pronounce Korean words. That’s because most of them are written the same way as they are pronounced.
Korean pronunciation
There are some exceptions, but overall, the pronunciation rules of the language are very simple and clear. You will not find tones in standard Korean, so getting started with speaking is quite effortless.
Korean can be written in English letters following an official romanization system. It’s useful for approximating words into English, but it’s not good for pronunciation.
How to Learn Korean
The best way to learn Korean is to learn some basic grammar and phrases and start interacting with people in Korean.
What is Korean grammar like?
The basic word order for Korean sentences is subject-object-verb. However, the word order in Korean is flexible, and the verb is often the only word you need for the sentence to make sense. Thanks to this, it’s easy to start creating sentences right away for beginners who want to practice the language. If you wish to start learning grammar today, start with our guide on Korean grammar for beginners.
There are nine parts of speech in the language. These parts are nouns, pronouns, numbers, action verbs, adverbs, descriptive verbs and adjectives, interjections and exclamations, particles and postpositions, and, lastly, determiners and indeclinable adjectives. If you know Japanese, you may recognize similarities in the grammar structure to Korean.
What are Korean honorifics?
Koreans use honorifics and speech levels to show the relationship between the speaker and who they’re speaking to or speaking of. Speakers need honorifics when talking of someone with higher status or older age. For example, you would make use of honorifics if you are talking about or to your parents.
Different speech levels are used depending on who you are talking to. If they are older and have a higher status than you, then 존댓말 (jondaetmal) should be used. That is because 존댓말 (jondaetmal) is the polite speech level. With friends and people younger than you, the informal speech level 반말 (banmal) can be used.
Additionally, there is a neutral speech level, which is used by speakers in general situations. This speech level may be used with people who are similar age and status to you but not a close friend (Note that Korean age is different than international age).
Does the Korean language have genders?
Technically, there is no gender in Korean grammar. This means words are not categorized separately, as in French, for example. And because you only need a verb in your sentence, you don’t need to write “he” or “she” in your sentence as you would in English.
However, by using 그 (geu) for a man and 그녀 (geunyeo) for a woman in your speech or text, you can make it clear whether you are talking about a man or a woman. Additionally, Korean vocabulary owns a lot of words that are specific to gender, such as 오빠 (oppa) for men, meaning big brother, and 언니 (eonni) for women, meaning big sister, or other familial titles that are specific to a gender.
What is Korean vocabulary like?
Korean vocabulary consists of native Korean words at its core. However, a lot of the vocabulary consists of words that were directly borrowed from the Chinese language.
There are many words that were adapted from Chinese characters. The exact amount of these words in Korean vocabulary is not known, but estimations vary from as low as 30% to as high as 65%. A few of the basic vocabulary you’ve already learned in Korean may have originated from Chinese words.
Borrowed Vocabulary Words
In addition to these words, as well as the previously mentioned loan words from English and Russian, the language has been borrowed from other languages. For example, some parts of the vocabulary come from Mongolian. And then, there are some new words that were adapted from the Japanese language, which in turn originated from German.
North and South Vocabulary Differences
This has led to additional differences in the vocabulary used in the South and in the North. North Korea has tried to implement as many native Korean words into daily practice as possible, decreasing the number of words taken from the Chinese language.
Thus, there are some popular vocabularies used in the North that do not exist in the South, and vice versa. Over the years, the two main Korean dialects have developed differences in pronunciation, spelling, and grammar.
Conclusion
That wraps it up for our write-up on Korean. Hopefully, you’ve enjoyed this and know a bit more about the language and culture. If you want to learn more, we’ve got some fantastic resources on things such as Korean slang, Korean phrases, and Korean numbers that you can put into action right away.
We also have a structured online Korean course that will teach you how to have a 3-minute conversation in the first 90 days.
Is there anything else that you’re curious about? Please let us know in the comments below!






Very thankful to u for these articles giving lot of motivations and encouraged me but by learning korean we still need to learn dialets?????
Great, thanks for the kind words! You can learn the dialects if you want but we suggest to learn the standard Korean.
Thank you very very very much… 90 Day Korean….
Your articles are too good for the basic knowledge and for further learning Korean language… I loved reading it thoroughly and not skipping… by this rate of curiosity and information you provide i think I’ll be able to learn Hangul very soon! Keep this good work of yours going… I appreciate your efforts… and I’ll use it very nicely. 감사합니다 😊😊
That’s great! It’s our pleasure. We’re glad that it has been valuable to you. ^^
Thank you for the article. it helped to reinforce what i have learned so far in my journey learning Korean and I feel encouraged to continue and perhaps one day achieve fluency in the language although it is a long way off.
Awesome! It’s our pleasure. We’re glad that it has been valuable to you. ^^
This is really useful. I am very keen to learn Korean now.
That’s great! ^^
How I can learn korean traditional thanks you
Sure, I’ll be glad to help. You can check on these two articles “South Korea – History, facts, and modern life on the peninsula” and “Korean Culture – Guide to History, Customs, People, and Modern Day” to help you learn Korean traditions.
https://www.90daykorean.com/korea/
https://www.90daykorean.com/korean-culture/
Have always been a fan of Korean in their language and in their culture since the age of 7yrs when I started watching kdramas and it has also pushed me to learn their language…… But now that have read your article it has encouraged me to thrive more for me to pronounce and speak fluently in Korean…. Keep up the good work….. 사랑해❣️❤️
Awesome, thanks for the kind words! We appreciate your feedback a lot. 화이팅 ^^