Want to learn about Korean numbers? You came to the right place, we’re going to teach you everything you need to know about how to count in Korean!
To start, here is a list of the basic Korean numbers:
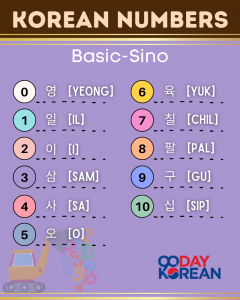
- 0 – 영 (yeong)
- 1 – 일 (il)
- 2 – 이 (i)
- 3 – 삼 (sam)
- 4 – 사 (sa)
- 5 – 오 (o)
- 6 – 육 (yuk)
- 7 – 칠 (chil)
- 8 – 팔 (pal)
- 9 – 구 (gu)
- 10 – 십 (sip)
We have a downloadable PDF resource that contains a list of Korean numbers. The PDF also has worksheets that you can use to practice the Korean numbers in the list. It also has an answer key for you to self-check your answers. Download the resource here and use it to study the numbers:
Let’s go!
Contents
- 1 Korean Numbers
- 2 Korean Counting
- 3 Korean numbers 1 -10
- 4 Korean numbers 1 – 100
- 5 Korean number chart
- 6 Korean Number System
- 7 The Sino-Korean Numbers System
- 8 Sino-Korean Numbers
- 8.1 Sino-Korean Numbers 1-10
- 8.2 Sino-Korean List of Numbers 1-100 and beyond
- 8.3 “Hundred” in Korean
- 8.4 “Thousand” in Korean
- 8.5 How to count money in Korean
- 8.6 “Ten thousand” in Korean
- 8.7 “Hundred thousand” in Korean
- 8.8 “Million” in Korean
- 8.9 “Ten million” in Korean
- 8.10 The Secret to Success: Count the Zeros
- 9 The Native Korean Numbers System
- 10 Native Korean Numbers
- 11 When to use Sino-Korean and Native Korean Numbers
- 12 Korean Ordinal Numbers
- 13 Korean Counters
- 14 Numbers in Korean
- 15 Korean Phone Number
- 16 Wrap Up
Korean Numbers
In this lesson, we’re going to teach you all about Korean numbers. It’ll help you a lot as you learn Korean.
We’ll start with the Korean numbers 1 to 100, and then learn to count to over a billion by only learning a few Korean counting words. This lesson will also give you exercises to help you check your understanding of the Korean number system.
Korean Counting
When counting in Korean, you will only need to learn around 35-40 numbers. Once you know those numbers, you’ll have everything you’ll ever need to count in Korean (including large numbers!).
Korean numbers 1 -10
When learning how to count in Korean, you’ll first learn the basic Korean numbers from 1 to 10, similar to how you learned counting in English. It’s easy to learn the rest of the Korean numbers if you know the first 10. You only need to learn a small group of numbers, and you’ll be able to count to a billion (and higher).
However, unlike in English, there’s a challenge with learning how to count in Korean. There are two different systems of numbers you need to know.
The first is the Sino-Korean number system. This number system involves the following numbers:
일 (il), 이 (i), 삼 (sam), 사 (sa), 오 (o), 육 (yuk), 칠 (chil), 팔 (pal), 구 (gu), 십 (sip)
And the second number system is the Native Korean number system. This number system includes:
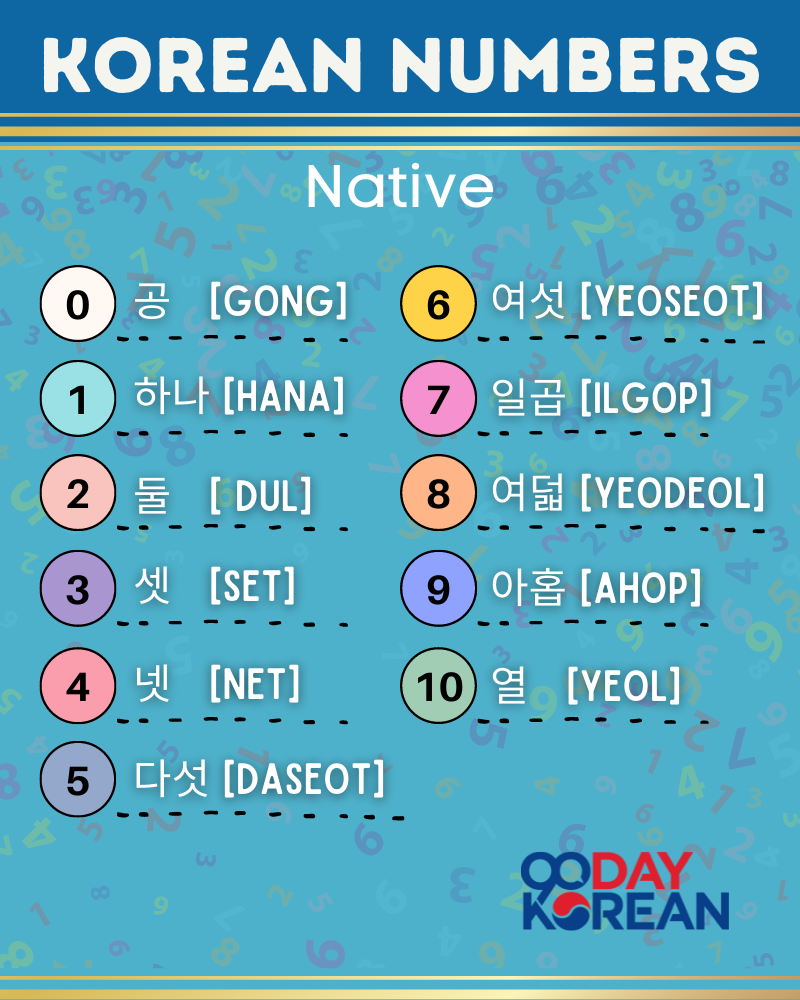
하나 (hana), 둘 (dul), 셋 (set), 넷 (net), 다섯 (daseot), 여섯 (yeoseot), 일곱 (ilgop), 여덟 (yeodeol), 아홉 (ahop), 열 (yeol)
Korean numbers 1 – 100
After learning the Korean numbers 1 to 10, the next thing to learn is the numbers 11 and up.
Although Koreans use two different number systems, learning numbers 11 and up is quite easy. This comes easy as long as you have the basic numbers 1 – 10.
All you need to do is to add up words from the basic numbers. For example, the number 11. This can be expressed as 십일 (sibil) in the Sino-Korean number system and 열하나 (yeolhana) in the Native Korean number system.
십일 (sibil) and 열하나 (yeolhana) were formed by adding Korean words from the basic numbers 1 – 10.
10 is 십 (sip) and 열 (yeol) and 1 is 일 (il) and 하나 (hana). Put them together, 십 (sip) + 일 (il) and 열 (yeol) + 하나 (hana) they become 십일 (sibil) and 열하나 (yeolhana).
Korean number chart
Let’s get started by taking a look at what we’re going to learn today. After going through the lesson, you should know all of these numbers in Korean. Below is a table of Korean words for the different numbers. You’ll learn them using the two Korean number system: The native Korean and the Sino-Korean system.
| Numeral | Sino-Korean (China System) | Native Korean (Korea System) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | ||
| 2 | ||
| 3 | ||
| 4 | ||
| 5 | ||
| 6 | ||
| 7 | ||
| 8 | ||
| 9 | ||
| 10 | ||
| 11 | ||
| 12 | ||
| 13 | ||
| 14 | ||
| 15 | ||
| 16 | ||
| 17 | ||
| 18 | ||
| 19 | ||
| 20 | ||
| 30 | ||
| 40 | ||
| 50 | ||
| 60 | ||
| 70 | ||
| 80 | ||
| 90 | ||
| 100 | ||
| 200 | ||
| 300 | ||
| 400 | ||
| 500 | ||
| 600 | ||
| 700 | ||
| 800 | ||
| 900 | ||
| 1000 | ||
| 2000 | ||
| 3000 | ||
| 4000 | ||
| 5000 | ||
| 6000 | ||
| 7000 | ||
| 8000 | ||
| 9000 | ||
| 10000 | ||
| 20000 | ||
| 30000 | ||
| 40000 | ||
| 50000 | ||
| 60000 | ||
| 70000 | ||
| 80000 | ||
| 90000 | ||
| 100000 | ||
| 1000000 | ||
| 10000000 | ||
| 100000000 | ||
| 1000000000 | ||
| 10000000000 |
We’re going to learn 20% of the words for numbers that are used 80% of the time. That will help us learn both small and large numbers quite quickly. But first, let’s learn about why there are two systems of Korean numbers.
Note: You can use 영 (yeong) or 공 ( gong) for zero. More on how to use the Korean numbers for zero below.
Korean Number System
I know what you’re probably thinking — “WHAT?! THERE ARE TWO KOREAN NUMBER SYSTEMS?!”
But don’t worry; it’s not all that bad.
To understand why two different number systems are used in Korean, it will help to go all the way back to the beginning for a mini-history lesson!
Over the years, the Korean language has developed two systems for numbering things, namely the Sino Korean system, and the Native Korean system.
Korea and China have a long history, and the first number system we’ll learn was derived from the Chinese characters (though the words themselves are uniquely Korean) of the Chinese language.
This is a fun and easy system to use because you can count up to very large numbers using it–all the way up to a billion and beyond! The numbers are quite simple. The words used for the set of numbers from 1-10, plus the numbers for 100, 1000, and even 10,000 are all only one-syllable words!
The Sino-Korean Numbers System
The first set of numbers is called the Sino-Korean numbers system. This set has its roots in Chinese numbers, so you might want to think of this one as using the “China System”. If you know the Chinese language, some of the numbers in this Korean number system may sound familiar to you.
Like China, this number system has a population of well over a billion. It is like the Great Wall of China — it stretches for many miles, but it is not very high in most places (ie., the words for its numbers don’t have many syllables). It’s beautiful in its simplicity, yet it serves a very important function.
To learn every number you’ll ever need to know in this Korean counting system, you only need to memorize 18 numbers.
That’s right! Learn the set of numbers 1-10 plus the words for hundred, thousand, ten thousand, and a few increments after that, and you can create all the other numbers easily through simple combinations.
That should be reassuring. Korean counting using the Sino-Korean numbers system is quite easy, even when you get to large numbers!
Imagine you were learning English for the first time now. You’d have to learn many more numbers than you would be using the Sino-Korean numbers system. That is because each multiple of ten has a new name in English.
In Korean, it’s just a matter of simple multiplication.
For example, 10 in the Sino-Korean number system is 십 (sip). 20 in Korean is literally “two-ten” (이십 | isip), 30 is “three-ten” (삼십 | samsip) and so on.
Likewise, 100 in the Sino-Korean numbers system is 백 (baek), while 200 is “two-hundred” (이백 | ibaek) and 300 is “three-hundred” (삼백 | sambaek).
And this pattern continues in the Sino-Korean numbers system even up into the billions. Just multiply or combine, and you’ve got yourself the number you’re looking for!
Knowing how easy it is to create numbers in Korean. Your only task becomes to memorize the critical 18 Sino-Korean numbers.
Sino-Korean Numbers
Sino-Korean numbers are numbers that have Chinese origins. They can be written using Chinese characters but the pronunciation is different from the Chinese language.
Sino-Korean numbers are used to express dates, money, minutes, addresses, and phone numbers.
Sino-Korean Numbers 1-10
First, let’s focus on the set of words used for numbers 1-10 in the Sino-Korean number system. We like to call these Korean words “The Magic 10” because once we have them memorized, we can use them to create new numbers out of — just like magic! Remember that this number system is called the Sino-Korean Numbers, or simply the Chinese numbers.
Here they are:
| English | Korean |
|---|---|
| ONE | |
| TWO | |
| THREE | |
| FOUR | |
| FIVE | |
| SIX | |
| SEVEN | |
| EIGHT | |
| NINE | |
| TEN |
There are many ways to memorize these core Sino-Korean Numbers 1-10. One is creating a peg system. This is just one method you may wish to use!
Just make sure to memorize those first sets of 10 Sino-Korean numbers before progressing in the lesson! Take your time and memorize them now.
Sino-Korean List of Numbers 1-100 and beyond
Now, equipped with the knowledge of Sino-Korean numbers 1-10, you can make all the Sino-Korean numbers from 1-99 through simple combinations. The smaller number always comes first. In other words, it’s “two ten,” not “ten two.”
We’re going to learn them as we go, but let’s get a quick preview of what we’re going to learn. Here are the remaining 8 numbers we need to learn to count in Korean to a billion and beyond!
In fact, if we just remember the words for one hundred, one thousand, and ten thousand, we are able to create combinations that create the other Sino-Korean numbers.
| English | Korean |
|---|---|
| ONE HUNDRED | |
| ONE THOUSAND | |
| TEN THOUSAND | |
| ONE HUNDRED THOUSAND | |
| ONE MILLION | |
| TEN MILLION | |
| ONE HUNDRED MILLION | |
| ONE BILLION |
Nice work on those Korean numbers!
As you can see, a pattern emerges for numbers greater than 10 and lower than 100.
First, you write the tens digit, and then you write the ones digit. If the number is greater than twenty, then the appropriate number is added in front of the tens digit to indicate.
For example, twenty is 이십 (isip) because it is “two tens.” Likewise, thirty is 삼십 (samsip) because it is “three tens,” and so on.
This makes it easier to count numbers in Korean than in English, where we have to memorize a new word for every “ten” less than 100.
“Hundred” in Korean
“Hundred” in Korean is 백 (baek).
This word will come in handy as you begin to count 100 and up. For numbers 100 to 199, you can have the word 백 (baek) and add the tens digit.
For example:
100 + 23 = 123
You can say this number as 백 이십삼 (baek isipsam).
For numbers 200 and up, it’ll be the same process as you do for the tens digits. For example:
200 → 이백 (ibaek)
250 → 이백 오십 (ibaek osip)
300 → 삼백 (sambaek)
345 → 삼백 사십오 (sambaek sasipo)
Just remember, start with the largest number.
If we were writing or saying this number in Korean, we’d start on the left and work our way right, one digit at a time.
RULE: If there is no tens digit, you just skip it and write the one digit.
It is the same as with English numbers. We wouldn’t write “one hundred, zero ten and one,” we just say “one hundred and one.”
The same rules apply to Korean numbers. You just write the numbers as you would in the English language.
“Thousand” in Korean
The Korean word for “thousand” is 천 (cheon).
You can listen to the clickable audio below for the pronunciation of the word:
In order to express other numbers in the thousands, you can begin by saying the largest number to the least. For example,
1500 → 천 오벡 (cheon obaek)
2000 → 이천 (icheon)
3300 → 삼천 삼백 (samcheon sambaek)
As you’re starting to get the hang of this, why don’t you try a few numbers exercises before we continue on? Remember — start on the left and work your way right when breaking down Korean numbers.
After that, the next significant number is ten thousand. Actually, this number is very significant in Korean culture.
How to count money in Korean
As you may know, the Korean currency is called the won.
₩ –>Korean won (원 | won)
The Korean won comes in 10 000 won increments, and although 50 000 won bills also exist, 10 000 won (만 원 | man won) bills are by far the most commonly used.
“Ten thousand” in Korean
The Korean word for the “ten thousand” is 만 (man).
Below is clickable audio to help you with the word’s pronunciation:
To say other numbers in the “ten thousand” place, you can add the largest number from left to right. For example,
20,000 → 이만 (iman)
30,000 → 삼만 (samman)
40,000 → 사만 (saman)
Let’s attempt to write some numbers you may possibly hear as the total when making a purchase at a retail store in Korea.
Just follow along with the same pattern we’ve been using, but this time, try adding the word “won” (원) at the end to indicate we’re talking about currency.
Notice that when it’s one hundred, one thousand, or ten thousand, you don’t need to say “one” in front of the number. In other words, one hundred won in Korean is 백 원 (baeg won), not “일백 원 (ilbaeg won).” Likewise, ten thousand won is 만 원 (man won), not “일만 원 (ilman won).”
The tricky part is going above ten thousand.
The higher numbers in Korean (one hundred thousand, a million, ten million, etc.) are calculated in increments of ten thousand.
In the English numbering system, we use thousands: one hundred thousand, ten thousand, and so on. But in Korean, they use ten thousand as the base.
This makes things tricky for native English speakers and native Korean language speakers alike to translate higher numbers quickly between the two different languages. But equipped with the right 80/20 knowledge, you can do it easily!
“Hundred thousand” in Korean
“Hundred thousand” in Korean is expressed as 십만 (simman).
Below is clickable audio for the pronunciation:
In the Korean language, using 10,000 units as a base, so we’d call hundred thousand as “ten (십 | sip) ten thousand (만 | man).” Makes sense; it’s 10 ten thousand units.
“Million” in Korean
“Million” in Korean is 백만 (baekman).
This can be thought of as “one hundred (백 | baek) ten thousand (만 | man)” since it’s 100 ten thousand units.
“Ten million” in Korean
“Ten million” in Korean is 천만 (cheonman).
천만 (cheonman) can be thought of as “1000 ten thousand units.”
The Secret to Success: Count the Zeros
The key to Korean numbers is to count the zeros.
Since we are using increments of 10 000, we know there are always four zeros at a minimum. Everything in front of the four zeros is the number we add in front of “만 (man).”
For example, for 10 000 000, we can take out the four zeros first since we know that indicates “ten thousand (만 | man).” Let’s do that now:
10 000 000
Then, we look at the number that is left over. In this case, it’s 1000:
10 000 000
One thousand in Korean is 천 (cheon), so it’s 천만 (cheonman). For a non-rounded number, you’d do the same thing!
With that little trick, it makes things a lot easier, doesn’t it?
Notice that when the numbers are not rounded numbers, the same rule still applies. Take out four digits on the right just as you would if the number was round, then start with the number left over on the left-hand side. Add 만 (man), and then finally, write the remaining numbers.
Next, we’ll learn the number for 100 000 000 (one hundred million). It has a special name in Korean and becomes the new base increment as the numbers get higher than one hundred million. It is called 억 (eok).
Just notice that in this case, one hundred million is written with “일 (il)” in front of it (unlike the numbers for one hundred, one thousand, or ten thousand).
Instead of taking out four zeros in this case, you’d just take out eight zeros, then write the number left over in front of “억 (eok).”
For example, you could write one billion:
With another zero, it would become . Add one more, and it’s 천억 (cheoneok). That’s 100 000 000 000! You just counted to 100 billion in Korean!
The higher numbers are commonly used for housing prices, monthly rents, and deposit amounts. Therefore, if you are planning to rent a house in Korea, you can put your newfound language knowledge to use!
As you can see, knowing just these 18 numbers can allow you to count in Korean all the way up to 1 000 000 000 and higher. Large numbers will be a breeze for you.
You’ve worked hard and deserve huge congratulations!
You previously learned how to count in Korean from one all the way up to a billion and beyond. It was hard work, but you made it!
Now you’re halfway there. Let’s move on to learn about the other system used for Korean numbers.
The Native Korean Numbers System
The Native Korean numbers system is a bit more modern than the Sino-Korean numbers system. Like the country of Korea, it has a much lower population (only 99 numbers, to be precise), and it tends to be more than one layer (many of the numbers are at least two syllables)!
You can think of this set of numbers as the “Korea System.”
The first number in the Native Korean numbers system is 하나 (hana), which is shortened to 한 (han) when counting in Korean.
This makes it easy to remember as the Native Korean numbers system, considering that 한국 (hanguk) means “Korea.” They have the same first syllable!
The Native Korean numbers system has more complex words for numbers, and they can be trickier to internalize at first.
It’s best to start with just the numbers 1-4 in the beginning, as these are what you’ll use most often. Luckily, these four Native Korean numbers are some of the easiest to learn and have fewer syllables.
After you are comfortable with these numbers, move on to learn the Native Korean numbers all the way to 10!
Though the set of numbers goes all the way up to 99, you will rarely ever use numbers greater than 10 with the Native Korean numbers system.
The exception would be when saying your age or hearing other people’s ages, so it is suggested you learn the Native Korean numbers 20, 30, and any other that is necessary for saying your age.
With the exception of these numbers, you’ll often hear most Koreans just using the simpler Sino-Korean numbers system when counting large numbers so it really isn’t necessary to learn the others unless you wish to for personal knowledge or the rare exception.
Well, those are the two systems, but we know you may have a few questions. Let’s F-A-Q this thing!
Why Are There Two Systems of Korean Numbers?
Consider it a thing of beauty, something that makes the Korean language unique.
Just as other languages have oddities or unique points that seemingly don’t make sense on the surface, Korea’s two number systems (Sino Korean system and Native Korean system) are a reflection of its rich history.
It evolved two number systems over time, and just know that learning both is important in order to get by in Korea!
Take it on as a challenge. By learning the second system of numbers, you’ll open up a whole new set of possibilities for yourself in terms of counting in Korean, ordering in restaurants, and many other practical uses!
How Do I Know Which Korean number System to Use?
The two Korean number systems are used at different times and for different purposes. One system will be used at a given time, depending on the purpose of communication. The only exception where the two systems are mixed is for telling time. We say the hours using the Native Korean numbers and the minutes using the Sino-Korean numbers!
The Sino-Korean numbers system is used for time (minutes), units of time, the names of months, money, saying phone numbers, measurements, and so much more!
Also, since the Native Korean numbers system only goes up to 99, it’s used for any number 100 or greater by default. It’s a very useful system!
On the other hand, the Native Korean numbers system is used for counting things and people, age, time (hours), and for counting in general!
For now, that’s your next mission — to count in Korean using the first set of numbers in the Native Korean numbers system.
How do you say zero in Korean numbers?
There are two different versions of “zero” for Korean numbers.
The first is 공 (gong), and the second is 영 (yeong) which is used with the Sino-Korean numbers.
You’ll use the 공 (gong) version of zero for things like phone numbers. For example:
010-1234-5678
공일공-일이삼사-오육칠팔 (gongilgong-ilisamsa-oyukchilpal)
010-6157-1700
공일공-육일오칠-일칠공공 (gongilgong-yukilochil-ilchilgonggong)
So, you’ll use 공 (gong) for zeros in phone numbers.
You’ll use the 영 (yeong) version of zero for things like math, temperature, and sports. It is part of the Native Korean number system. If you visit Korea during the winter, you may be surprised to hear that the weather report is 영하십도 (yeonghasipdo | minus 10 degrees)!
On occasion, you may also hear the Konglish version of zero, which is 제로 (jero).
Native Korean Numbers
Native Korean numbers are numbers that originated in Korea. They are written and read in Korean.
The Native Korean numbers go up to 99. From 100 onward, you would use the Sino-Korea numbers.
Native Korean numbers are used for counting. They’re used to count people, hours, things, ages, and others.
Native Korean Numbers 1 to 10
All these numbers doing a number on you? Don’t worry!
Though you only had to memorize 17 words using the Sino-Korean numbers system to be able to count to a billion, it should be reassuring to know that you need to learn even less to know the whole Native Korean numbers!
In fact, knowing only a few of the numbers in the beginning, will allow you to do the majority of what you’ll need to do with this system, so start slow and focus first on memorizing the numbers 1-4.
When you’re feeling ambitious, move all the way up to 10.
To get started, let’s take a look at the numbers 1-10 in the Korean System.
| English | Korean |
|---|---|
| ONE | |
| TWO | |
| THREE | |
| FOUR | |
| FIVE | |
| SIX | |
| SEVEN | |
| EIGHT | |
| NINE | |
| TEN |
Go ahead and start committing this set of Korean numbers to memory.
They are slightly more complex than the Sino-Korean numbers system, with more than half of them having two syllables.
You may wish to use a peg system or create visual associations for easier memorization of the numbers. Or, you may have a system of your own!
Can you think of any possible links for the numbers to English words you already know? How about a “duel” for 2 (둘 | dul)? A “hobbit” swinging on a vine for 9 (아홉 | ahop)? Be creative and make some associations. It helps!
Memorize the most critical numbers 1-4 first, then move on to the rest. When you get there, move on to the next section.
But before you do, go reward yourself for your hard work.
Native Korean Numbers 10-100
Once you have the numbers 1-10 down, the rest is easy.
Just like the Sino-Korean System, we combine the numbers to create the numbers 11-19. In this sense, 11 is literally “ten one”, 12 is “ten two,” and so on.
Knowing this, it should be easy. Try to write the numbers 11-19 now.
As a review, also write that set of numbers using the Sino-Korean System.
Practicing them side-by-side as you’re learning them makes it easier to understand the structure of the numbers and also makes it less likely you’ll mix them up in real-life scenarios later on.
Things work really similarly to the Sino-Korean numbers, don’t they?
However, unlike the Sino-Korean numbers, the Native Korean numbers have unique names for each multiple of ten, starting from twenty.
But as we previously mentioned, you don’t need to memorize them all! You will rarely (if ever) come across the higher numbers, and a lot of Koreans are switching to using the Sino-Korean numbers for the numbers higher than 30 anyway.
Twenty and thirty are still common, though, so you should commit them to memory! Here’s the word for twenty:
Give this a try yourself! Once you have the number memorized, you just add the ones digit to the end to form the appropriate number between 21-29. For example:
21 = 20 (스물 | seumul) + 1 (하나 | hana) ➜ 스물하나 (seumulhana)
22 = 20 (스물 | seumul) + 2 (둘 | dul) ➜ 스물둘 (seumuldul)
23 = 20 (스물 | seumul) + 3 (셋 | set) ➜ 스물셋 (seumulset)
…and so on!
Next, let’s learn “thirty” using the Native Korean numbers. You may need it from time to time! Here it is:
Counting in the thirties is just the same as we previously learned: Just tack on the ones digit at the end, and you’re all set!
31 = 30 (서른 | seoreun) + 1 (하나 | hana) ➜ 서른하나 (seoreunhana)
32 = 30 (서른 | seoreun) + 2 (둘 | dul) ➜ 서른둘 (seoreundul)
33 = 30 (서른 | seoreun) + 3 (셋 | set) ➜ 서른셋 (seoreunset)
…all the way up to 39!
Learning the rest of the numbers is really not necessary, but there really aren’t too many more to go. Remember, the Native Korean numbers only go up to 99!
But we use the Native Korean numbers to indicate our age as well, and that’s another one of the times you’ll use it on a regular basis! As you know, age is extremely important in Korean society.
The only larger number you may wish to learn is the tens digit for your age if you are older than 39 (or are soon to be, in which case we wish you an early happy birthday)!
Learn the tens digit for your age to start so you can answer the common question in Korea, “how old are you?”
Here are the numbers for your knowledge.
| English | Korean |
|---|---|
| FORTY | |
| FIFTY | |
| SIXTY | |
| SEVENTY | |
| EIGHTY | |
| NINETY |
That’s it! You can fill in the gaps by using the ones digits to create all of the other numbers.
It’s nice when the counting system only goes up to 99, isn’t it?
Just recall that two major uses for this system will be to say our age and to count things.
So as a final test, say your age in Korean using the Korean System of numbers!
When to use Sino-Korean and Native Korean Numbers
Now that we know the Korean numbers and how to count in Korean, it’s just a matter of knowing when to use which system of numbers. We’ve given a brief overview of when they’re used in this lesson.
In general, we use the Native Korean numbers system for things like saying your age and counting in Korean. It is also used for talking about the number of people.
We use the Sino-Korean numbers system most often for things like the date, a period of time, distance, and money. For telling time, a combination of the Native Korean and Sino-Korean systems would be used.
Korean Ordinal Numbers
Ordinal numbers are used to indicate the position or order of items in a sequence. In English, these are the words “first,” “second,” “third,” and so on.
In Korean, there are two ways to write these numbers:
- Number + 번째
- 제 + Number
The difference is that 번째 (beonjjae) is a pure Korean word, while 제 (je) is sino-Korean word.
제 is more formal than 번째. So 제 + number is often used in written form, such as in books or formal documents. For example, 제 1 장 means “the first chapter”. When using 제, the number should be read using China number system, like “제 일 장”.
In everyday conversation, 번째 is commonly used. When using 번째, numbers are read with Korea number system, except the first, one hundredth, and higher. “First” is 첫 번째 (cheot beonjjae), not 한 번째 (han beonjjae). This is because the Native Korean number system is only used from 1-99.
Basic Ordinal Numbers in Korean
Korean ordinal numbers have a unique structure compared to English. Here’s a list of the basic Korean ordinal numbers from first to tenth:
| Korean Ordinal Numbers | English Translation |
|---|---|
| 첫 번째 | First |
| 두 번째 | Second |
| 세 번째 | Third |
| 네 번째 | Fourth |
| 다섯 번째 | Fifth |
| 여섯 번째 | Sixth |
| 일곱 번째 | Seventh |
| 여덟 번째 | Eighth |
| 아홉 번째 | Ninth |
| 열 번째 | Tenth |
Korean Ordinal Numbers 11th to 20th
Now that we’ve covered the basics, let’s move up to the next level. Here’s what the Korean ordinal numbers from 11th to 20th look like:
| Korean Ordinal Numbers | English Translation |
|---|---|
| 열한 번째 | Eleventh |
| 열두 번째 | Twelfth |
| 열세 번째 | Thirteenth |
| 열네 번째 | Fourteenth |
| 열다섯 번째 | Fifteenth |
| 열여섯 번째 | Sixteenth |
| 열일곱 번째 | Seventeenth |
| 열여덟 번째 | Eighteenth |
| 열아홉 번째 | Nineteenth |
| 스무 번째 | Twentieth |
Korean Ordinal Numbers 100th to 1000th
For the Korean Ordinal numbers from the 100th, we already use the China Number System. This is because Korea system numbers only exist from 1-99.
| Korean Ordinal Numbers | English Translation |
|---|---|
| 백 번째 | One hundredth |
| 백일 번째 | One hundred first |
| 백이 번째 | One hundred second |
| 백삼 번째 | One hundred third |
| 백십 번째 | One hundred tenth |
| 백이십 번째 | One hundred twentieth |
| 천 번째 | One thousandth |
Korean Counters
There are special Korean counting words that you can use for specific items. These counting words are known as Korean counters.
For example, if you’re talking about people, you use the counter 명 (myeong).
학생 두 명 = 2 students
For animals, you’ll use the counter 마리 (mari).
강아지 세 마리 = 3 dogs
**Note: When using the Native Korean numbers with counters, the first 4 numbers 하나, 둘, 셋, and 넷 becomes 한, 두, 세, and 네.
For example:
피자 하나 조각 (pija hana jogak) (X)
피자 한 조각 (pija han jogak) (O)
These are special cases. You should change these for any numbers that end in 1- 4. For example, you’d use 열한개 instead of 열하나 개. The rest of the numbers will stay the same.
We have a full list of counters and the corresponding number system here.
Using counters and numbers for ordering
By knowing just the first number, you can now order something and properly indicate how many of that item you want! This will help tremendously with learning Korean since it will get you talking.
Need a caffeine boost? Head to the nearest coffee shop, such as Starbucks, walk up to the barista, and say:
“아이스 아메리카노 하나 주세요 (aiseu amerikano hana juseyo).”
Please give me one iced Americano.
If you’re a latte drinker, it doesn’t matter! Order your favorite drink, and add in the number (e.g.,하나 | hana) afterward to indicate how many you want.
This is one major reason we need the Korean system — these numbers help us count and indicate how many of something we want!
Numbers in Korean
There are a few different words for “numbers” in the Korean language. It depends on the usage or the situation.
The word for “numbers” in Korean is 숫자 (sutja).
For example:
숫자가 맞아요. (sutjaga majayo)
The numbers are right.
The word 번 (beon) can be used to talk about things like “number of times” or “number of tries”.
For example:
어제 너한테 두 번 전화했었어요. (eoje neohante du beon jeonhwahaesseosseoyo.)
I called you twice yesterday.
You can also use 번호 (beonho) to refer to things like phone numbers or passwords. The word 번지 (beonji) is used for street numbers on a house, while 호 (ho) is used to refer to an apartment number.
Another word used for “number” is 수 (su). You can express the number of something by adding the word 수 (su) after a noun. For example, 직원 수 (jigwon su) for “number of staff” and 승객 수 (seunggaek su) for “number of passengers.”
As a summary, the word “numbers” in Korean can be expressed with the following words:
- 숫자 (sutja)
- 번 (beon)
- 번호 (beonho)
- 번지 (beonji)
- 수 (su)
Korean Phone Number
Korean phone numbers can be divided into 2 sections; mobile phone numbers and telephone numbers.
Telephone numbers in South Korea are made up of 7 – 8 numbers. If you’re going to call a telephone number using a mobile phone, you’ll need the country code, the area code, and the 7-8-digit number.
South Korea mobile phone numbers are made up of 11 numbers, beginning with 010. The number 010 is a prefix for mobile phones. If you’re going to call a mobile phone number in South Korea, you’ll need to add the country code +82.
How to read Korean Phone Numbers
When reading phone numbers in Korean, you’ll read them using the Sino-Korean numbers.
For example, the mobile phone number 010-5394-2178.
You’ll read this number as 공일공-오삼구사-이일칠팔 (gongilgong-osamgusa-iilchilpal).
Another example is the telephone number +82 (2) 8765-4213.
You’ll read this as 팔이-이-팔칠육오-사이일삼 (pali-i-palchilyuko-saiilsam)
How to ask for someone’s phone number in Korean
If you’re going to ask for someone’s number, you can ask either of these questions:
전화 번호가 몇 번이에요? (jeonhwa beonhoga myeot beonieyo)
What is your phone number?
전화 번호가 어떻게 되세요? (jeonhwa beonhoga eotteokke doeseyo)
What is your phone number?
핸드폰 번호가 몇 번이에요? (haendeupon beonhoga myeot beonieyo)
What is your cell phone number?
Wrap Up
Learning Korean numbers will become second nature once you start adding them to your daily life. They will be especially helpful if you visit Korea or want to start understanding K-dramas without subtitles. Combine numbers with common Korean words and phrases, and you’ll be well on your way to having conversations in Korean! But if you want to create clear and more accurate Korean conversations, you can also learn about the basics of Korean sentence structure.
If you’re ready to take things to the next level, you may wish to join our Inner Circle Korean language Web Course, where we give you weekly lessons, accountability, personal coaching, and live monthly training to keep you motivated along the way to Korean language learning!
We hope this lesson was valuable to you! Let us know your favorite Korean numbers (written in Korean of course) in the comments below.








Thank you . It’s help to learn it very well 😎💪
Sure, it’s our pleasure. We’re glad that it has been valuable to you. ^^
No one can explain better than this, thank you for this😊😊
Sure, it’s our pleasure. We’re glad that it has been valuable to you. ^^
It’s really useful. Thank you.
That’s great! It’s our pleasure. We’re glad that it has been valuable to you. ^^
i thought the numbers were
0- yeong
1- hana
2- dul
3- set
4- net
5- daseot
6- yeoseot
7- ilgop
8- yeodeol
9- ahop
10- yeol
many apps and sites have said those ;-; im still learning but still-
That’s correct, Elias! There are two number systems in Korea as listed above, and the one you typed is the Native Korean Numbers System! ^^
thankyou so much for this!!🥰
Sure, it’s our pleasure. ^^
Thank you so much this is really helping me 🥰❤️ thank you again 😊💗
Sure, it’s our pleasure. We’re glad that it has been valuable to you. ^^